YOUR CART
- No products in the cart.
Subtotal:
₹0.00
BEST SELLING PRODUCTS
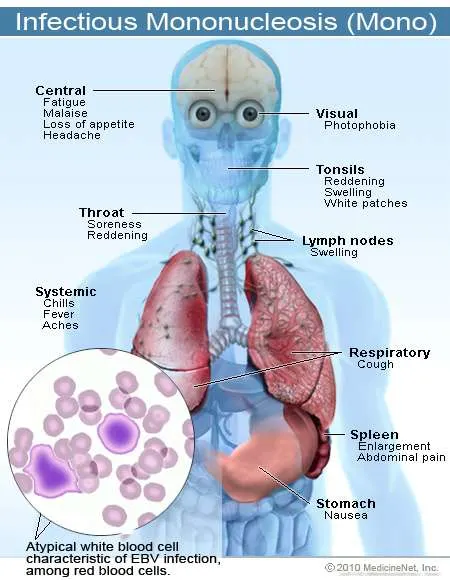
Kissing disease:?A name for?infectious mononucleosis?(“mono”), a very common illness caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). By the time most people reach adulthood, an antibody against EBV can be detected in their blood meaning they have been infected with EBV. The illness is less severe in young children. The infection can be spread by saliva. The incubation period for “mononucleosis” is 4 to 8 weeks. Symptoms include?fever, fatigue,?sore throat, and swollen lymph glands. “Mononucleosis” can cause liver inflammation (hepatitis) and spleen enlargement. Vigorous contact sports should be avoided to prevent spleen rupture.
Mono?(also termed?mononucleosis?or infectious mononucleosis) is a disease caused by the?Epstein-Barr virus?(EBV). Children are commonly infected with EBV and show few or no symptoms. Older individuals, teenagers, and adults may show symptoms when infected. These consist mainly of?fatigue,fever, inflamed throat, and?swollen lymph nodes?in the neck. Infected people may also have a?rash, swollen?liver, or?enlarged spleen. Most of the symptoms get better within two to four weeks, but some people can be fatigued for several months. The EBV virus can become inactive after infection, and some people reactivate EBV infection even years later.
Mononucleosis is contagious?from person to person, especially via an infected person’s saliva. Other transmission methods include blood, semen, blood transfusions, and organ transplants. Unfortunately, EBV can also be spread by contact with objects like toothbrushes or eating utensils that are contaminated with EBV. Mononucleosis can be spread to?babies, children, and ?adults. Individuals who have mono can be contagious without the characteristic symptoms of?fever,?fatigue, or swollen glands; some people can be contagious during the incubation period when no symptoms are present.
Symptoms of EBV infection/Mononucleosis may include some or most of the following symptoms:
Many diseases produce similar symptoms, so the diagnosis is usually based on the patient’s history, physical, and EBV antibody tests (for example, IgG, IgM, and VCA antibody tests, Monospot test, and others). Interpretation of these tests is not always definitive.
Mono (mononucleosis) is spread from person to person. It is usually not spread by airborne droplets (it can be in some instances when saliva is sprayed and then inhaled) but by direct contact with an infected person’s saliva. Because of the predominant way mono is spread (saliva), it has been termed the “kissing disease.” The incubation period (from time of exposure to EBV to symptom development) is about four to seven weeks, and some people can spread the disease during the incubation period and up to 18 months later. Mononucleosis can be spread by blood, semen, and organ transplants. Saliva-contaminated toothbrushes, utensils, and contact with other EBV-contaminated objects may also spread the disease.
Fortunately, the more severe complications of mononucleosis are quite rare, and mononucleosis is very rarely fatal in healthy people. The rare severe complications include destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia) and inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart (pericarditis), the heart muscle itself (myocarditis), and the brain (encephalitis). Mononucleosis tends to be more aggressive in patients with abnormal immune systems, such as people with AIDS or those who are taking medications that suppress immune function.
Unfortunately, the term “cured” doesn’t relate well to mono (mononucleosis) because, once infected, a person seems to be infected with EBV for life as occasional “reactivation” of the virus does occur even in healthy people who show no symptoms. Most people will never notice the reactivation of EBV, but according to researchers, these reactivated?viruses?are probably responsible for the occasional outbreaks in individuals who have not been infected with EBV. It’s estimated that about 20%-80% of people infected with mononucleosis shed EBV occasionally for many years.
What is the Treatment for Kissing Disease /Mononucleosis/Infectious Mononucleosis?
Principle of treatment for mononucleosis is preventive and palliative.
Preventive treatment for mononucleosis : Advise every healthy as well as infected person to observe oral hygeine ….saline water gargling , dental and gum brushing and massage and further gargling before and after kissing.One should avoid random multipeople kissing.Forbid and avoid kissing the toddlers and children despite any loving/affectionate emotions.
Palliative treatment for mononucleosis :
Rx? GULVALEX 1 capsule three to four times a day for 50 to 90 days with water for building up immunity and resistance against infections.


Rx? HEMOCLIN-T 1to 2 tablets three to four times a day for 50 to 90 days with water for combating? infections due to viruses and bacteria.
Rx AAROGYA VARDHINI VATI 500mg 1 to 2 tablets 2 to 3 times a day for 50 to 90 days to keep the blood,cells ,tissues,liver and digestive organs in good health
