YOUR CART
- No products in the cart.
Subtotal:
₹0.00
BEST SELLING PRODUCTS
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease known also as:Disseminated Sclerosis or Encephalomyelitis Disseminata that attacks the central nervous system. It affects the insulating cells of the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a potentially disabling disease of the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
In MS, the immune system attacks the protective sheath (myelin) that covers nerve fibers and causes communication problems between your brain and the rest of your body. Eventually, the disease can cause the nerves themselves to deteriorate or become permanently damaged.
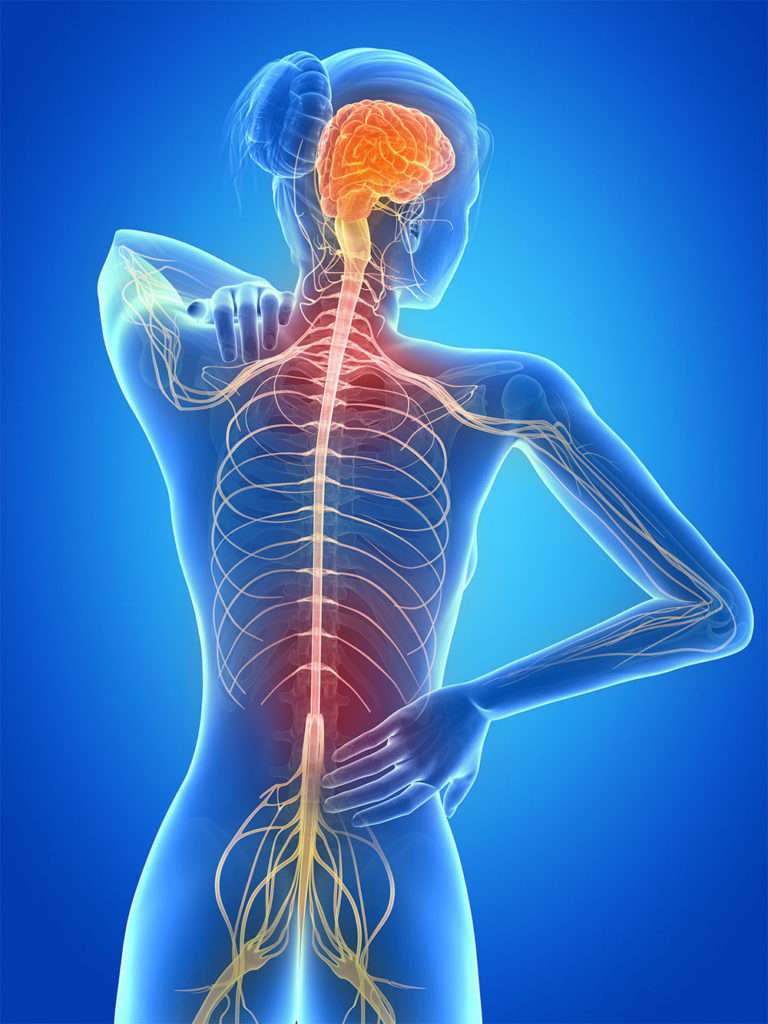
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
Signs and symptoms of MS vary widely and depend on the amount of nerve damage and which nerves are affected. Some people with severe MS may lose the ability to walk independently or at all, while others may experience long periods of remission without any new symptoms. For some patients, symptoms are so mild that they do not notice anything until later in the course of the disease. Others may be aware of their symptoms in the early stages.
There’s no cure for multiple sclerosis. However, treatments can help speed recovery from attacks, modify the course of the disease and manage symptoms which may include:
What is the sex ratio of Multiple Sclerosis?
It is two to three times more common in women than in men, and diagnosis usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 50 years.
Most people with MS have a relapsing-remitting disease course. They experience periods of new symptoms or relapses that develop over days or weeks and usually improve partially or completely. These relapses are followed by quiet periods of disease remission that can last months or even years.Small increases in body temperature can temporarily worsen signs and symptoms of MS, but these aren’t considered disease relapses.
About 60 to 70 percent of people with relapsing-remitting MS eventually develop a steady progression of symptoms, with or without periods of remission, known as secondary-progressive MS.The worsening of symptoms usually includes problems with mobility and gait. The rate of disease progression varies greatly among people with secondary-progressive MS.
Some people with MS experience a gradual onset and steady progression of signs and symptoms without any relapses. This is known as primary-progressive MS.
These factors may increase the risk of developing multiple sclerosis:
People with multiple sclerosis also may develop:
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that attacks the central nervous system. It affects the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves.
Symptoms range widely. In milder cases, there may be numbness in the limbs. Severe cases may involve paralysis or vision loss.
It is not possible to predict how multiple sclerosis (MS) will progress in any individual.
It is two to three times more common in women than in men, and diagnosis usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 50 years.
Fast facts on Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS): This is a single, first episode, with symptoms lasting at least 24 hours.
Relapse-remitting MS (RRMS): This is the most common form, affecting around 85 percent of people with MS and involving attacks of new or increasing symptoms.
Primary progressive MS (PPMS): Symptoms worsen progressively, without early relapses or remissions. Around 15 percent of cases are PPMS.
Secondary progressive MS (SPMS): After initial episodes or relapse and remission, the disease progresses steadily.
These can lead to :-
Bladder problems: There may be difficulty emptying the bladder completely, frequent urination, and urge incontinence
Bowel problems: Constipation can lead to fecal impaction, and this can lead to bowel incontinence.
Fatigue: This affects up to 90 percent of patients, and it can undermine their ability to function at work or at home.
Dizziness and vertigo: These are common problems, along with difficulties with balance.
Sexual dysfunction: A loss of interest in sex is common in both males and females.
The doctor will carry out a physical examination, ask about symptoms, and consider the patient’s medical history. No single test can confirm a diagnosis, so several strategies are needed when deciding whether a patient meets the criteria for a diagnosis.
There will be a neurologic exam, imaging scans, a test to measure the electrical activity of the brain, a spinal fluid analysis, and possibly other tests. These can help rule out other possible causes of the symptoms.
Several disease-modifying and symptomatic relief giving drugs are useful for the relapsing forms of MS.

GULVALEX: Herbal immuno-modulator …improves the tissue-cellular structures. Dose 1 to 2 capsules three to four times a day with water or milk for long time.
AZARAQI extule : 1 capsule three to four times a day for nerve stimulation,for long times.


VIGOPROT : 10 gm twice or thrice a day for nutritional deficiencies.
DYNOGESIC liniment : Locally used application for allaying pains
